Unit 1B, Keynor Farm
Sidlesham, PO20 7LL
8:30am - 5:00pm
Monday - 4:00pm Friday
Blog
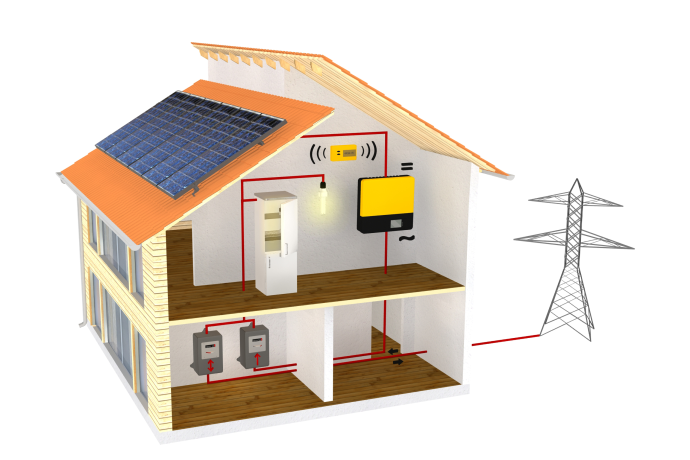
Battery Storage. Your questions answered.
In this blog we will be looking at some of the FAQs surrounding grid-tied battery storage systems installed alongside Solar.
How Does Battery Storage Work?
Battery storage is simply a way of storing surplus energy produced by a renewable energy source. Most commonly storage is use in conjunction with solar PV, this will form the basis of this blog.
When a solar array is producing more energy than a property is using this energy is exported to the national grid. Storage sits within the system to capture any un-used energy. When usage is higher than renewable generation power will be exported from the batteries rather than imported from the national grid.
There are 2 main ways of adding storage to a property with a solar array, AC Coupled or DC Coupled. Although very similar the equipment used, and some of the working parameters are different.
A key benefit of storage is its modular capability. This means you can easily have a smaller storage system for a domestic property, or a large system for commercial use.
Another benefit is the ability of some equipment to provide a UPS function. This is basically the ability for some circuits within a property to be fully powered just by the batteries should there be a power cut. Not all equipment has this function, and it isn’t a standard feature of battery systems, a common mis-conception. Having batteries installed also does not mean you are ‘Off-Grid’, the equipment used still needs to be grid tied, and must meet stringent testing to be allowed to perform in the way that it does.
The last major benefit of storage is the way it can be used to save money on your bills. A well designed and well set up storage system can save money on electricity bills by reducing the amount imported from the grid.
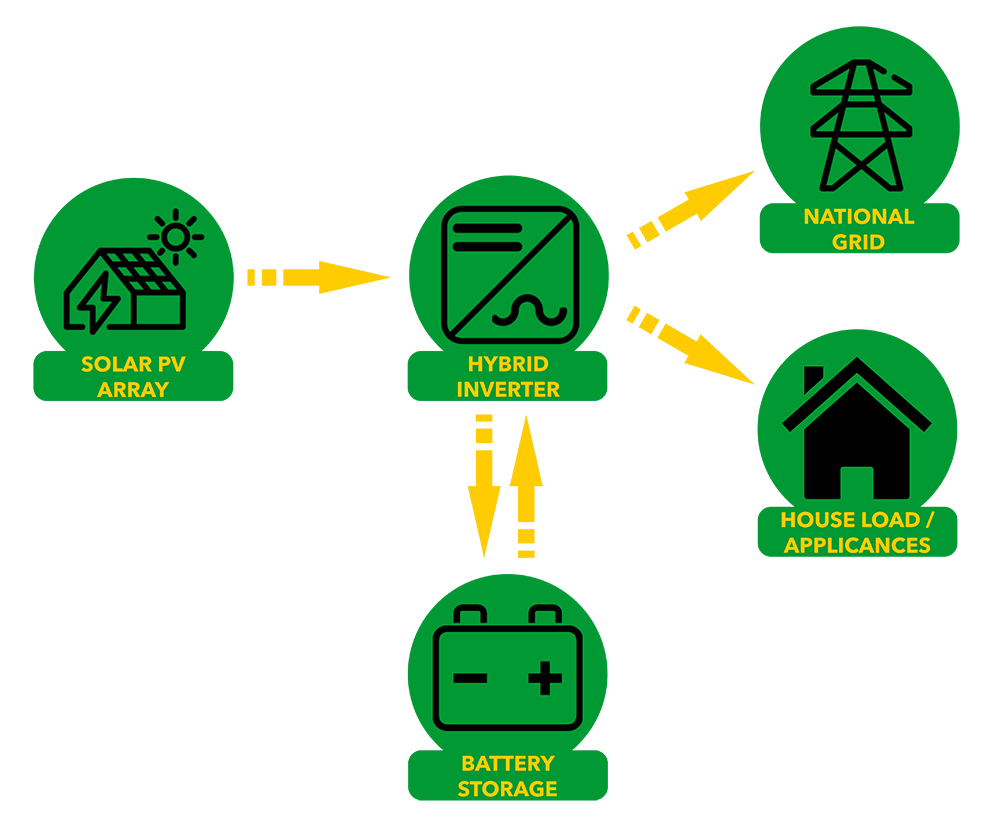
Designing a Battery Storage System.
As mentioned a well designed storage system can help you save money on your bills. Key considerations are the size of the solar array, the amount of surplus electricity / amount exported to the grid. We also take into account other technologies used within the renewables system, e.g. Immersion Controllers, and Electric Vehicle Chargers. This will give us an idea of the size of the battery storage, and the way it can be used.
When looking to add storage into a system as a retro-fit we will look at current solar generation and export figures. In some cases we may suggest adding a monitoring device onto your system to get accurate figures.
As solar is often modular you can always add more to your system. It can often be beneficial to downsize the storage if you’re not and add more at a later date! The larger the storage capacilty the more solar you need in order to charge it. One popular brand name storage system contains 13.5kWh of storage. We’ve calculated that in order to charge 13.5kWh of storage you would need 12.7kW of solar PV*. Most domestic properties only have around 4kW of solar PV so a smaller storage capacity of 2.4kWh to 7.2kWh is often more appropriate.
How much does storage cost?
One of the most popular questions. Storage has come down in price a lot over the past few years, it still remains an investment. Cost will ultimately depend on the size of your system and which features you would like it to have.
If retro-fitting battery storage into an existing system (depending on the set up and inverter already in place) a 4.8kWh storage system can typically cost between £2400 – £3000. This is based on the installation of a new storage inverter.
If adding into a new system the costs can vary, but typically remain at around the £3000 mark.
Is Battery Storage Worth it?
With decreasing prices and increasing technological advances battery storage has certainly become viable.
Early adopters of the Feed-In-Tariff scheme could have storage added to their system and see this paid back in a matter of years thanks to the deemed export scheme, and Feed-In-Tariff payments. For those not on the FIT storage is much more about energy saving and using the batteries as a household appliance.
As mentioned earlier a key benefit of storage is it’s ability of reduce your electricity bills. Rather than sending surplus electricity back to grid and earning 5p per unit (based on average SEG figures) and then having to buy that back at 14p per unit you can store that energy effectively for free.
Other options that are possible is flexible tariff charging, with the grid becoming smarter many companies are offering variable tariffs. This allows batteries to be charged at a cheaper tariff, that energy can then be used when the tariff is higher. This is particularly useful in the winter when solar generation is often lower. Some companies are also allowing batteries within a SEG paying system. Meaning those who sign up for the SEG can still receive payments for energy exported from a battery system. You can read more about the SEG in our blog here; The Smart Export Guarantee.
Installing Battery Storage In Your Property
Battery Storage systems should always be installed by trained electricians who are familiar with the equipment they are installing. Our electrical engineers are fully trained to install battery storage into new or existing systems. All of our storage installations are registered with Flexi-Orb, and come with an insurance backed guarantee.
If battery storage is something you would like to explore further contact one of the team for more information or a free no-obligation quote; Contact Us.



